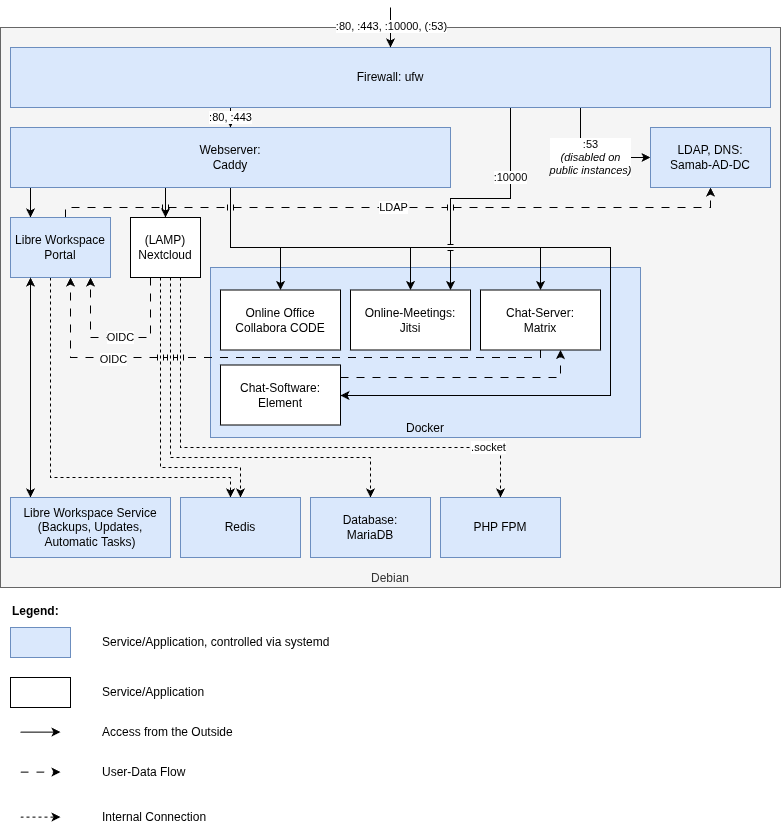
General Architecture
Overview
Libre Workspace forms a collection of applications on top of Debian while using common services to provide a seamless experience and an automated cloud environment for users and administrators. Regular Debian stable is used as a base operating system. While Libre Workspace also runs on selected Ubuntu servers, Debian is the preferred OS for production systems.
As a basic firewall implementation, UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) is used to protect the system from unwanted access. Please be aware that some applications might overwrite UFW rules, like Docker. For more information, please refer to the respective application documentation. Therefore, for bigger production instances, a dedicated firewall in front of the server is recommended.
As a web server, Caddy is used to provide secure access to all the different web applications via HTTPS. By default, for public access, a free certificate from Let’s Encrypt is used. For internal networks, Caddy generates its own certificates. The root certificate can then be downloaded from e.g. cert.int.de, which is considered a private URL by Libre Workspace.
One central service is Samba-AD-DC, which provides LDAP and Kerberos services for authentication and user management. DNS services are also provided by Samba-AD-DC.
For some applications, Redis is installed and secured with a password to provide caching services to improve performance and concurrency.
On top of all these services, the Libre Workspace Management Layer is installed to provide automated installations of all above-mentioned applications and services as well as all following applications. This layer consists of two different parts: - The Libre Workspace Portal itself provides a web interface to manage users, groups, backups, applications, and addons, and implements services like REST API, OIDC, and 2FA. It is the “visible” part of the management layer. - The Libre Workspace Service is a background service running automated tasks for simple monitoring, backups, updates, and other maintenance tasks. It is included with the libre-workspace-portal package and is mandatory for a Libre Workspace Environment. - On top of that, some simple CLI tools are provided for easier automation for addons and administrative tasks. All these commands start with “libre-workspace” and are located under /usr/bin/
One other essential part of a Libre Workspace environment is the Docker Engine. Many applications like Matrix, Jitsi, or Guacamole (part of the Cloud Desktop) are running inside Docker containers to provide better isolation, easier updates, and simpler maintenance. Almost all Docker containers are managed by docker-compose files which are in subfolders of /root/
Last but not least, Libre Workspace provides a LAMP stack (Linux, Caddy, MariaDB, PHP-FPM) to run web applications like Nextcloud. This LAMP stack is only installed if the Nextcloud module is installed.
On top of these services and applications, you are free to install/integrate other applications as needed. The whole system is designed to be modular and is not as opinionated as you might assume from a preconfigured system.
Here is an overview of the general architecture of Libre Workspace. It is meant to give you an idea of how the different components interact with each other but may not show every detail of the implementation: